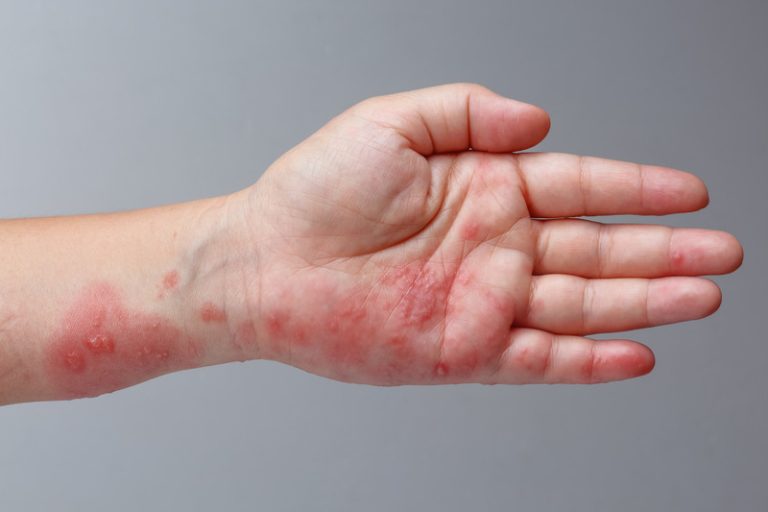
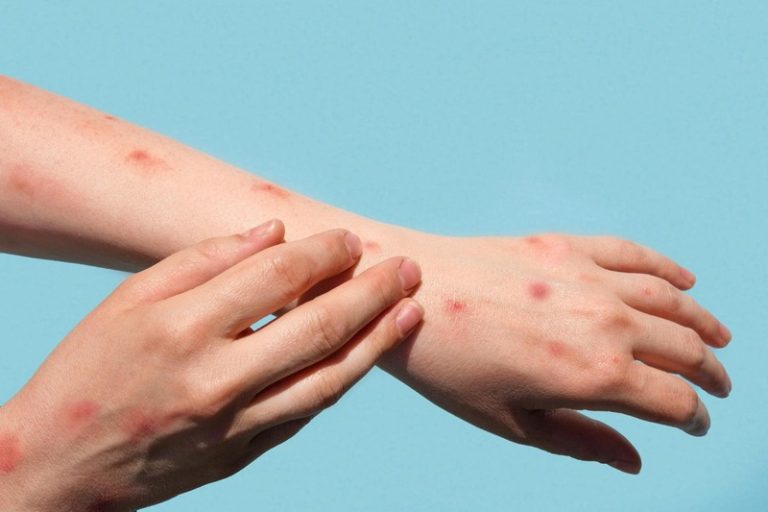
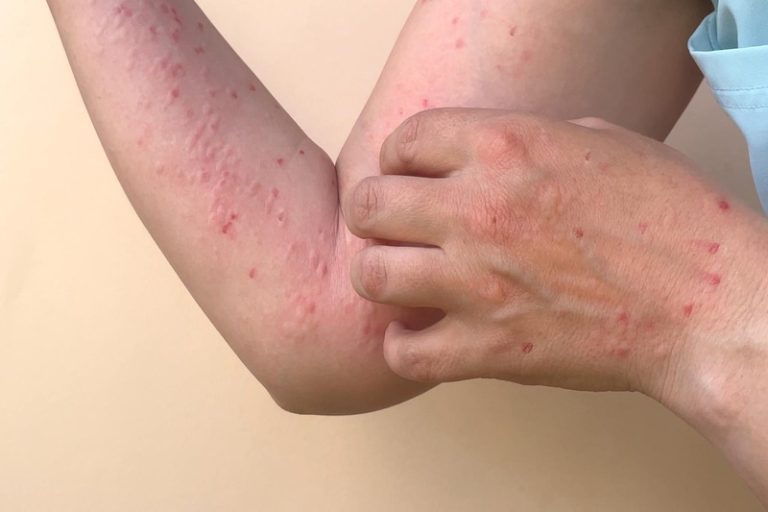
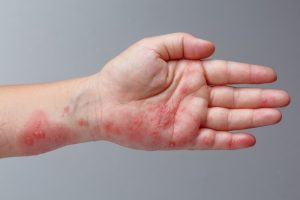
Treatment for skin infections at Skinpase Clinic
What is Skin Infection?
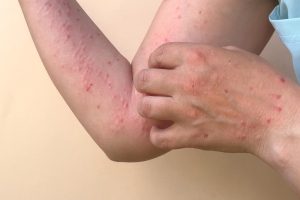
A skin infection can result from a bacterial, viral, or fungal growth affecting your skin or occasionally the tissues below it. It can also develop when a parasite gets underneath your skin in some settings. Your chance of getting an infection rises when your skin is wounded by a cut, tattoo, piercing, sting, or bite.
Infections can occasionally start close to the skin’s surface, even though they could develop further deeply inside the wound. While less severe skin infections can often be treated at home, more severe ones can necessitate a visit to the ER or doctor.
Keep an eye out for these symptoms if you suspect an infection on your skin:
- Pus or liquid dripping from the wound
- Red skin surrounding the wound
- A pimple or yellowish crust on top of the cut, with a red track running from it toward your heart
- Bruises that resemble blisters
- Intensifying pain
- Swelling that worsens a few day by day
- Fever
- The wound is still not healed after a week.
Common Types of Skin Infections
Skin Fungal Infections (mycosis)
Skin, hair, nails, and mucosal tissue can all be affected by fungus infections. Based on the area affected and the severity of the illness, symptoms vary in intensity. This could manifest as white lesions on the tongue, unusual vaginal discharge, crooked or discoloured nails, scaling, swollen glands, or hair loss around the head or beard.
Fungal diseases can be in a variety of forms. The following list includes some of them:
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
- Tinea Capitis ( Scalp )
- Onychomycosis(Nail)
- Tinea Versicolor
- Cutaneous Candidiasis
- Tinea barbae ( Beard )
Treatment for Skin Fungal Infections
Skinpase provides best treatment for skin fungal infections. The category of fungus involved determines the course of treatment for the infection. It can take a couple of days or a month to recover from a minor fungal infection. On the other hand, the average recovery time from deep tissue fungal infections is close to two years.
People who have a weaker immune system, high blood sugar, and a history of excessive use of antibiotics, steroids, and antiseptics are more vulnerable to developing fungus infections. It might be challenging to get rid of the fungus that causes these diseases. Treatment for skin fungal infections will be more challenging if you’ve already used topical steroids. In order to find successful treatment alternatives, it is always preferable to see a dermatologist.
Bacterial infections
A bacterial infection occurs when a dangerous bacterial strain multiplies on or inside the body. Bacterial infections can affect any area of the body.
The various bacterial species that can cause infections include:
- Staphylococcus
- Streptococcus
- Pseudomonas
- Clostridium difficile
- Escherichia coli(E.coli)
- Listeria monocytogenes
Treatment for Skin Bacterial infections
Antibiotics are administered topically, orally, or intravenously for the treatment of bacterial skin infections. However, this relies on the infections causing strain. They interfere with the activities required for bacterial cell development and proliferation. The bacterial infection could worsen if antibiotics are not taken exactly as directed.
Note: To avoid the problem from getting worse, stay away from topical antiseptic treatments and steroid-based therapies.
Viral infections
The conditions that are caused by viral skin infections are numerous. They could result from an infection of your skin or could be a reaction to a virus that is already present within your body. From very safe to quite serious, they come in many shapes and sizes (but not usually life-threatening). Some diseases are contagious through contact, whereas others are not.
Virus infections that spread easily include the following:
- Wart
- Molluscum
- Varicella Zoster (Chicken pox).
- Genital Wart.
- Herpes Zoster/Shingles (Non contagious)
Due to the fact that many presenting symptoms are similar, early detection improves the odds of effective treatment, which stops the transmission.
Treatment for Skin Viral infections
The treatment for skin viral infections varies depending on the specific virus causing the infection. Some common treatments include:
- Antiviral medications: For skin infections caused by viruses such as herpes simplex, antiviral medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir can help reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks.
- Topical treatments: For viruses such as molluscum contagiosum, topical medications can be used to treat skin lesions.
- Surgical removal: In some cases, such as with HPV-related warts, surgical removal may be necessary to remove the infected tissue.
- Cryotherapy: This treatment uses cold temperatures to freeze and remove the affected skin tissue.
It’s important to consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations, as well as to rule out any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the infection.
If you are struggling with other skin conditions like acne scars, keloids, psoriasis, skin tags or skin allergies, our doctors in the medical dermatology department will help you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are skin infections treated?
Treatment of skin infections relies upon on the sort and severity of the contamination. Infections are normally handled with antibiotics. Fungal infections are usually handled with antifungal medicinal drugs, both topical and oral. For mild infections, topical medications which includes lotions, creams, and ointments can be used. In more excessive cases or if the contamination has spread to a big vicinity, oral medicines such as antibiotics, antibiotics, or antifungals can be prescribed and in some cases a mixture of topical and oral sellers can be used.
In addition to medicines, treating dermatitis may also include taking steps to alleviate signs such as pain or ache, which include taking pharmaceutical painkillers or anticonvulsants.Moreover, follow the prescribed treatment plan and complete the full course of medication to ensure complete eradication of the infection and prevent recurrence.
What are the possible complications of untreated skin infections?
If left untreated, skin infections can result in a number of problems, like:
- Spread of the infection: Skin infections can unfold to more areas of the body causing substantial infection
- Scarring: Some skin infections results scarring or disfigurement, specifically if the infection is deep or significant.
- Systemic infection: In extreme instances, skin infections can result in a systemic infection called sepsis, which may be life-threatening.
- Abscesses: Pockets of pus called abscesses can form inside the infected place, which needs to be removed surgically.
- Chronic infection: Some skin infections can emerge as continual, leading to persistent symptoms and long-term damage to the skin or underlying tissues.
It is essential to seek clinical attention if you suspect you have skin infection, specifically if you have signs consisting of fever, redness, swelling, or ache which can be getting worse or no longer improving with treatment. Early analysis can help prevent complications and ensure a faster healing.
Can skin infections be prevented?
Yes, skin infections can often be prevented by following desirable hygiene practices and taking steps to keep away from exposure to infectious sources. Some methods one should follow to get protected from skin infections are:
- Wash your hands frequently: Regular hand washing with soap and water can save you the spread of infectious agents
- Keep skin smooth and dry: Keeping skin smooth and dry can assist to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi that may cause skin infections.
- Avoid sharing private gadgets: Avoid sharing objects which include towels, razors, and apparel, as those items can unfold infectious dealers among humans.
- Wear protective clothing: When participating in activities that may cause skin abrasions or cuts, inclusive of sports activities or gardening, wear defensive clothing to prevent publicity to infectious agents.
- Avoid near contact with inflamed individuals: Avoid near touch with people who have pores and skin infections, and avoid sharing non-public objects with them.
By following those suggestions, you could lessen your threat of developing skin infections and save you from the spread of infectious agents that may cause these infections.
Can skin infections be contagious?
Yes, many skin infections are contagious and can be spread from person to person through direct or indirect touch with the infected individual or their infected belongings. Ringworm, impetigo, scabies, and certain sorts of fungal infections are contagious skin infections. It is vital to take precautions to avoid spreading or contracting skin infections, which includes washing your arms frequently, getting into near contact with infected individuals, and not sharing personal gadgets which include towels or razors.
How long does it take for a skin infection to heal?
The time it takes for a skin infection to heal depends on the sort and severity of the infection, in addition to the individual’s normal fitness and immunity strength. Mild skin infections, which include impetigo may additionally start to cure within some days and may be fully healed in a week or two. However, more extreme or deep infections may take several weeks to absolutely heal. In some cases, the restoration process take longer period if the immune system is weakened, especially in people who’re taking medications that suppress the immunity.It is important to follow the prescribed medications of the healthcare provider to make sure the infection is completely treated and prevent recurrence.
Can skin infections recur?
Yes, skin infections can recur if they’re not completely handled or if the underlying reason of the infection isn’t properly addressed. Incomplete or insufficient treatments can cause the infection to persist and potentially recur, in particular if the bacteria, virus, or fungus causing the skin infection is not completely eradicated. Additionally, some skin infections might also recur if the underlying factor that led to the preliminary infection isn’t addressed, including poor hygiene or exposure to infectious agents. It is important to comply with the prescribed treatment plan and take steps to keep you hygienic and address underlying fitness conditions to reduce the chances of recurrence. If the skin infection does recur, you should take medical attention and prevent potential complications.
Latest Blogs
Updated Blogs & News
In recent years, cosmetic dermatology has undergone a remarkable transformation, introducing a plethora of cutting-edge treatments.They have altered our approach...
Our skin is the largest organ on our body and it’s the first thing people notice of our health or...
Looking to achieve a more youthful and Healthy Skin? If yes, you should strongly consider Laser skin resurfacing. By eliminating...
Introduction The quest for perfect, radiant skin is an aspiration shared by many individuals round the world. Skin pigmentation problems...
The sun is a powerful force that can be both beneficial and dangerous to our health. Sunlight is...
Thread veins and varicose veins are two types of veins that can cause discomfort and embarrassment. Thread veins...